panchalhimself
Backup and Restore k8s cluster data using etcd
16 June 2023
etcd is one of the core k8s components that stores cluster data.
So what are we going to do ?
-
We will manually backup the etcd cluster data to a file.
-
Delete the etcd data dir and make it corrupt.
-
Restore the etcd cluster data from the backedup file.
We will utilze etcdctl utility to perform the backup and restore.
We will setup the 3 node k8s cluster from the k8s-1.4 notes.
Fetch the cluster name : -
ETCDCTL_API=3 \
etcdctl get cluster.name \
--endpoints=https://IP_CONTROL_NODE:2379 \
--cacert=/PATH/TO/THE/etcd-ca.pem \
--cert=/PATH/TO/THE/etcd-server.crt \
--key=/PATH/TO/THE/etcd-server.key
Backup the cluster data : -
ETCDCTL_API=3 \
etcdctl snapshot save /PATH/TO/SAVE/BACKUPS \
--endpoints=https://IP_CONTROL_NODE:2379 \
--cacert=/PATH/TO/THE/etcd-ca.pem \
--cert=/PATH/TO/THE/etcd-server.crt \
--key=/PATH/TO/THE/etcd-server.key
Note: the above steps are executed from the etcd installation
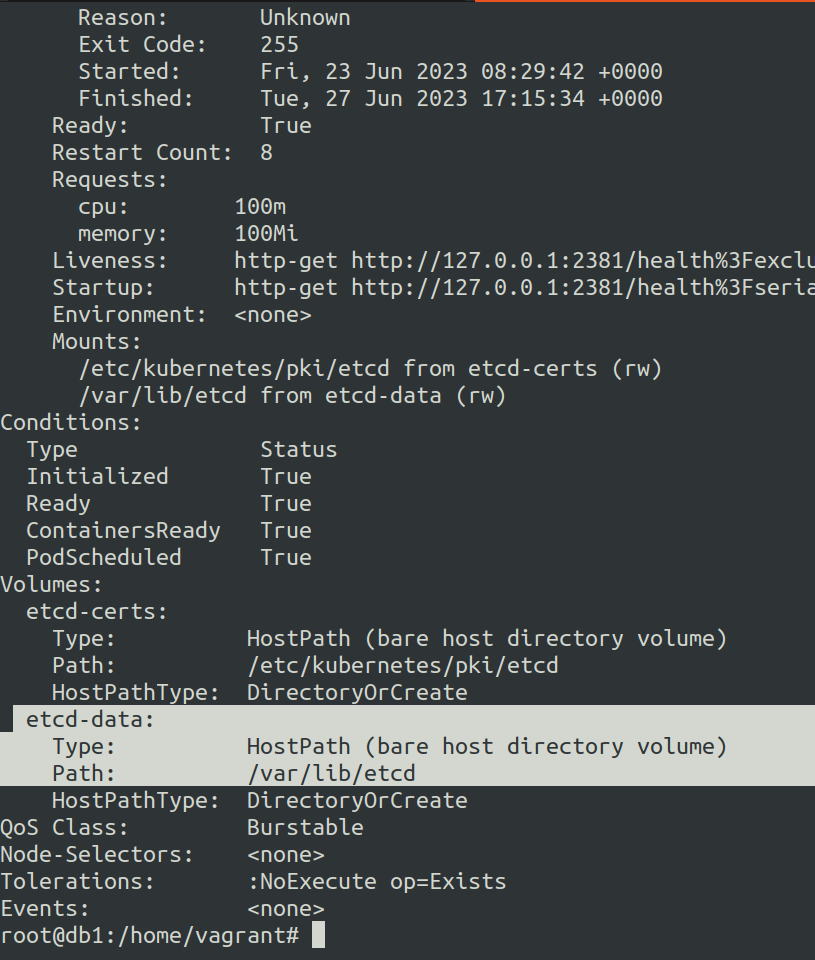
However when you have etcd running as a pod in the cluster, you can checkout the path of the --cacert, --cert, --key using kubectl describe on the etcd pod in the kube-system namespace.
etcd pod
etcd pod describe
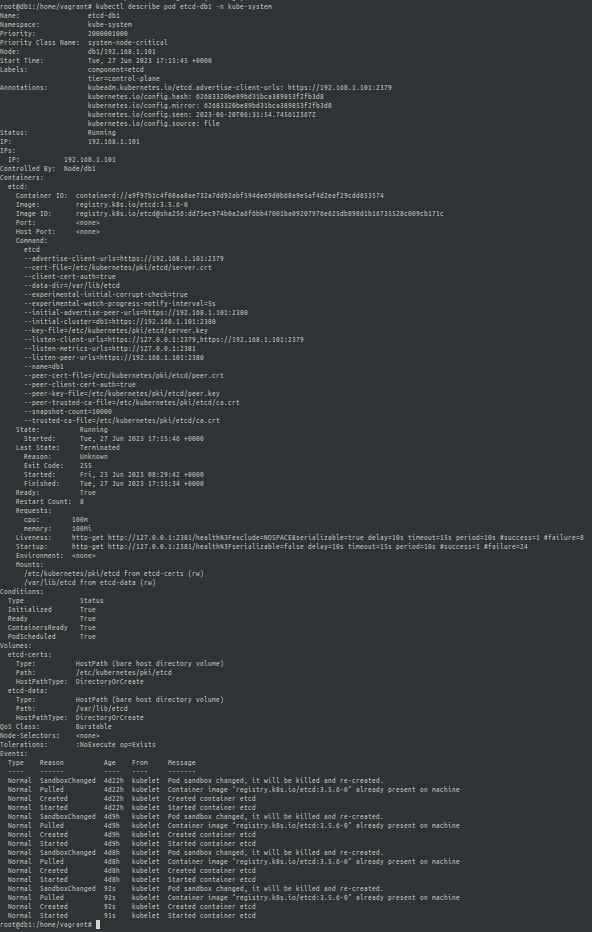
etcd pod describe the path to --cacert, --cert, --key
restore the etcd data dir using the stored file backups
You can restore the etcd cluster data using etcdctl snapshot restore /PATH/OF/BACKUP/FILE command on the etcd data dir or via direct command.
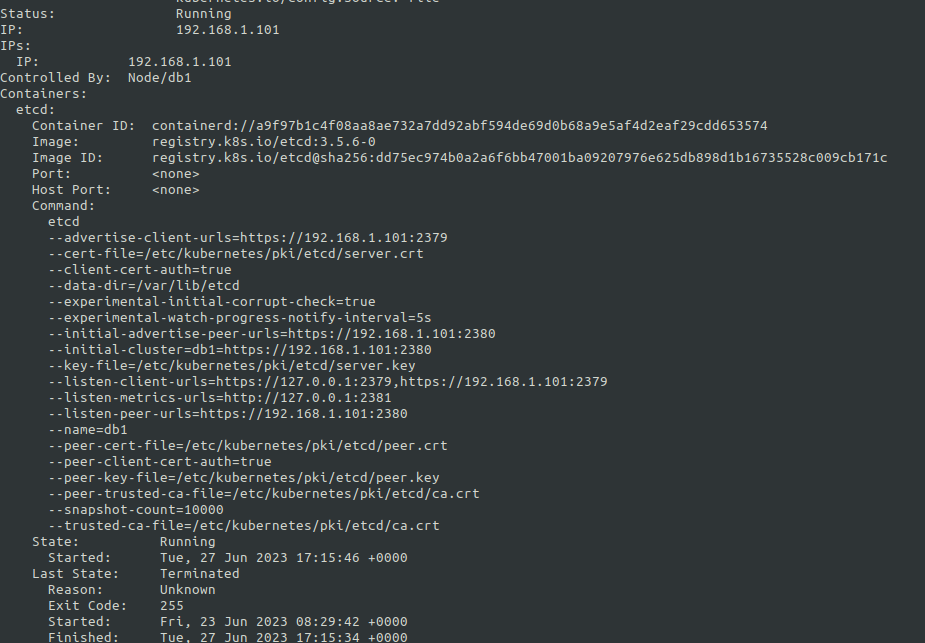
Now where is this etcd data dir on the cluster if it is running as a pod ?
etcd data dir
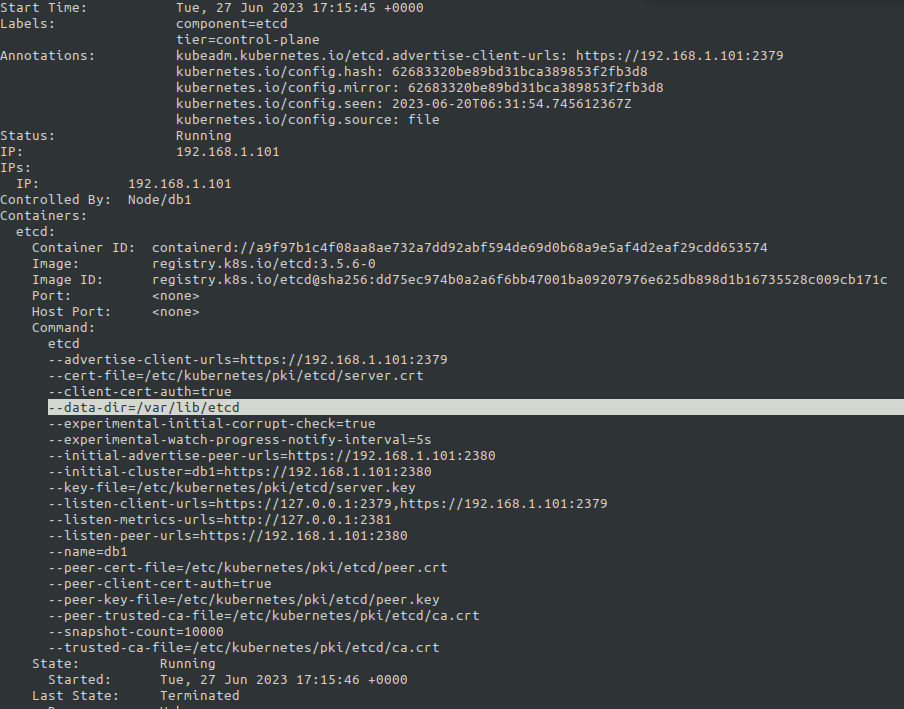
In the above case the etcd data dir is located at /var/lib/etcd` on the control plane node.
so in order to restore the backup properly you need to go to the etcd data dir and run the etcdctl restore /PATH/OF/BACKUP/ command.
This will create a folder whose content we need to move to the /var/lib/etcd
by default there is a folder named member at /var/lib/etcd which we need to replace with the one generated using etcdctl restore /PATH/OF/BACKUP/ command.
or
the most easiest and fastest way is using the command
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --endpoints=https://192.168.1.101:2379 --key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key --cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt snapshot restore /opt/mybackup
Example of a simple backup and restore
So in this example we will do the following:-
-
Take initial backup of the etcd cluster with 0 pods running in the default namespace.
-
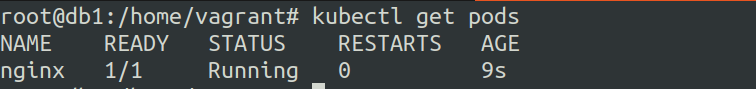
Run 1 pod.
-
Restore the etcd cluster to the initial backup state.
Now if you are in the control node chances are that you might not have etcd-client installed on the node as etcd is running inside a pod.
To keep things quick and easy you should install etcdctl using etcd-client package via your relevant package manager.
apt-get install etcd-client
Now let us take a backup.
In order to take backups you need to ensure that you have access to the control node.
For backups you need
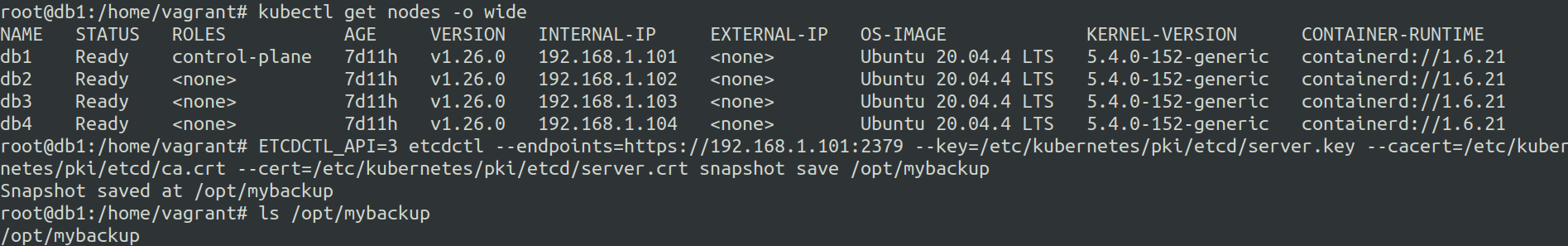
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --endpoints=https://192.168.1.101:2379 --key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key --cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt snapshot save /opt/mybackup
all we need is access to --key, --cert and --cacert path along with the --endpoints
Cluster state before backups on the default namespace.
Taking backup
Creating a nginx pod

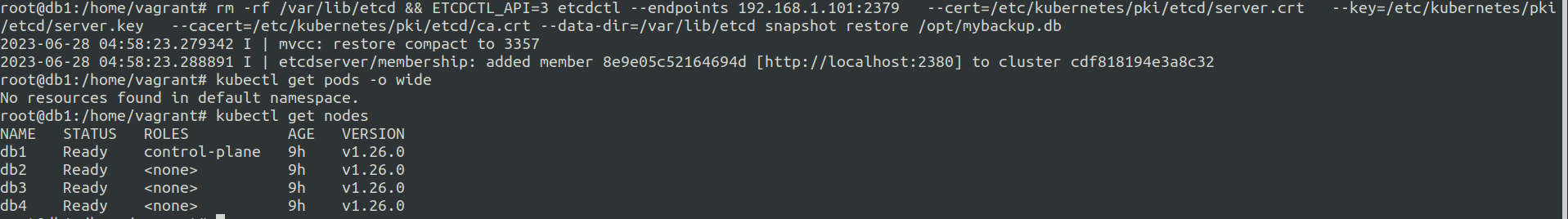
Now let us restore the cluster state to the backed up point.
Once we do this there should be no pods running.
So the etcd data dir is located at /var/lib/etcd after we did kubectl describe ETCD_POD -n kube-system
Restore using the command etcdctl snapshot restore /BACKUP/PATH/FILE
rm -rf /var/lib/etcd && ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --endpoints 192.168.1.101:2379 --cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt --key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key --cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt --data-dir=/var/lib/etcd snapshot restore /opt/mybackup.db
search_query: etcd backup
ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-upgrade-etcd/